What is Fungal Acne?
Fungal acne is a common condition many struggle to understand and overcome without access to proper treatment. When a patient seeks a professional opinion, it is vital to correctly diagnose the yeast overgrowth that causes fungal acne, to best determine the appropriate course of treatment.
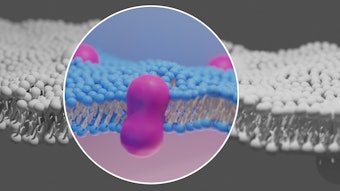
Malassezia yeasts are naturally found on the body and near the hair follicles. When there is an overgrowth of this yeast inside the hair follicles, it can lead to inflammation of the pore and present as pustules, papules and nodules— all of which can be tender to the touch. The most common symptoms of fungal acne are itching and clusters of these small red bumps on the face, chest, back, neck and arms. The location variance depends on the patient, as fungal acne can present anywhere with hair follicles on the body.
Yeast traditionally thrives in warm and moist environments, which means it can quickly multiply on hot and sweaty skin for extended periods. Malassezia overgrowth is also commonly seen in patients with immunosuppression and those on antibiotics. While antibiotics are a trusted and necessary treatment for many bacterial infections, they are known to decrease the amount of good bacteria everywhere in the body, which can lead to an overgrowth of yeast. Therefore, treating fungal acne comes down to targeting the source of yeast overgrowth.
Oral Treatment Options
1. Fluconazole and Itraconazole
Oral prescriptions for fungal acne are usually the first treatment course explored for a patient who presents with a case of fungal acne, regardless of the severity. Oral solutions are very effective because they target fungal cells’ growth and function, which traditionally leads to yeast overgrowth on the skin. Fluconazole and Itraconazole are the two most common prescriptions for fungal infections, including Malassezia yeast overgrowth. While side effects are rare, patients should know that nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headaches and dermatitis are all possible adverse reactions to the medication. It is important to advise patients on the best practices for taking the medication based on their prescription strength and to ask patients if they are on any anti-infectives that may inhibit the effectiveness of the anti-fungal prescription.
2. Accutane
Another oral solution that can be explored for patients with fungal acne is Accutane. As established, fungal acne is due to an overgrowth of yeast, which feeds on sebum naturally produced in the skin’s pores. Accutane eliminates the sebum-producing function of these glands, effectively cutting off the nutrient source to the yeast spores and helping combat the development of papules. However, Accutane is not without its side effects and should only be explored when other oral and topical solutions are exhausted for your patient.
Topical Treatment Options
3. Benzoyl Peroxide
An over-the-counter benzoyl peroxide is a good starting point for patients, and they may have even tried this before the consultation. While benzoyl peroxide is an effective bacteria-eliminating agent, it does not contain the necessary anti-fungal properties to address the root of the yeast overgrowth on the patient’s skin. If looking to include benzoyl peroxide in a treatment plan, a cleanser containing the active agent will best be used alongside an anti-fungal cream or gel applied after cleansing.
4. Anti-fungal Medications
Antifungal skin creams should be the cornerstone of a curated skin care regimen for patients who present with fungal acne. Econazole and ketoconazole are two standard options that should begin to clear symptoms in 2-4 weeks when used as prescribed. It is best to provide instructions to the patient for application based on what area of the body has the breakouts. For example, if the acne pimples are on the back, the patient will likely want to wear loose-fitting cotton clothes to avoid irritation after applying the product. While relatively uncommon, allergic and adverse reactions may occur, so it is crucial to ensure that patients are well-informed. Topical antifungal agents combined with oral antifungal treatments are shown to help expedite treatment results for patients, so it is worth exploring multiple treatment options at once for more severe cases of fungal acne.
5. Sulphur Treatment
Lastly, sulphur is another topical ingredient that is often essential for treating fungal acne. The combination of antibacterial, anti-fungal and sebum-reducing properties makes it the ideal treatment for acne vulgaris and yeast overgrowth causing fungal acne. Here, the application will be crucial for patient results. Ensure you direct patients on adequately applying either a sulphur-based cream or mask so that the skin can absorb the anti-fungal properties. These treatments should always be applied to a clean face, and with consistent use, results are often seen in 4-6 weeks. Sulphur masks and creams can also be combined with the former two treatment options – just be sure to advise patients based on their unique skin type.
The Diagnostic Process
A diagnostic process is the key to helping patients combat their acne conditions. Knowing the signs and symptoms of fungal acne and how it interacts with traditional acne treatments is crucial for identifying underlying causes. When patients present issues related to those pesky uniform papules and pustules, they may be struggling with Malassezia yeast overgrowth. As many medical providers know, there is no one size fits all solution for fungal acne, especially when a patient also struggles with bacterial or hormonal acne. Knowing the compounding effects of the differing topical and oral solutions out there can help you better tailor skin care treatments to your patient’s needs.
--
Samuel Hetz, M.D., M.Sc. is the Medical Director of Concept Medical. Concept Medical is a physician-led medical aesthetic and cosmetic dermatology practice. Dr. Hetz has undergone extensive training in primary care dermatology and aesthetic medicine, including neuromodulators such as Nuceiva®, Botox Cosmetic®, soft tissue filler treatments, as well as the delivery of energy-based technologies.