Research conducted in August 2023 on the safety of JAK inhibitors found the incidence of serious conditions did not increase significantly in JAK inhibitors-exposed patients with atopic dermatitis. The study was conducted by researchers from Pusan National University led by associate professor Yun Hak Kim and their findings were published in the Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology & Venereology.
Related: American Academy of Dermatology Updates Guidelines for Management of Adults with Atopic Dermatitis
Typical Uses of JAK Inhibitors
JAK inhibitors are widely used for the treatment of atopic dermatitis. However, the safety of these drugs for AD treatment has not been well examined until recently. Researchers have now comprehensively assessed the safety profile of JAK inhibitors by analyzing the results of 14 randomized controlled trials. Their study revealed that JAK inhibitor use is not associated with a greater risk of serious adverse events like malignancy, thromboembolism or major adverse cardiac events.
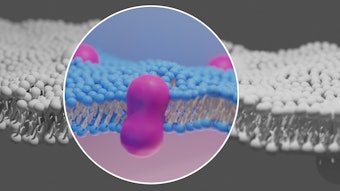
JAK inhibitors are small molecules that act by blocking the JAK family kinases and inhibiting the inflammatory pathways involved in atopic dermatitis and other inflammatory diseases. JAK inhibitors have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylarthritis, COVID-19, and atopic dermatitis, among others.
The FDA also issued a boxed warning for JAK inhibitors to include the risk of major adverse events, but the analyses of the adverse reactions required further research to solidify the connection.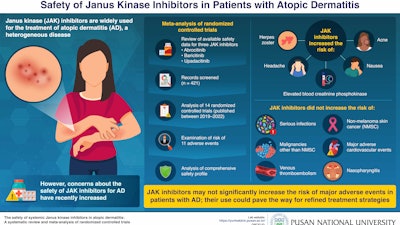 Photo courtesy of Pusan National University
Photo courtesy of Pusan National University
The Study
The systematic review and meta-analysis by Kim, et. al, examined whether the use of JAK inhibitors increased the occurrence of adverse events in patients with atopic dermatitis. They identified studies reporting the adverse events associated with JAK inhibitor use from Medline, Embase and Clinicaltrials.gov, among others for this study. They then analyzed the risk of 11 adverse events from 14 RCTs published between 2019 and 2022.
Their analysis revealed that the relative risk of developing herpes zoster, headache, acne, elevated blood creatinine phosphokinase and nausea increased among those patients with atopic dermatitis who received treatment with JAK inhibitors. However, the incidence of serious conditions did not increase significantly in JAK inhibitors-exposed patients with atopic dermatitis.
Recent reports suggested that the adverse effects of JAK inhibitors may be dose-dependent, so the researchers also conducted a subgroup analysis of the safety profile of these inhibitors according to the JAK inhibitor type and dose.
They looked at three types of JAK inhibitors—abrocitinib, upadacitinib and baricitinib. Although baricitinib has yet to receive FDA approval, the drug is clinically approved for the treatment of atopic dermatitis in European countries, Japan and Korea, per the study.
Takeaways
This analysis revealed a higher risk of acne in patients receiving upadacitinib and abrocitinib, although the increase in risk was dose-dependent. Higher doses of JAK inhibitors were correlated with an increased risk of acne and elevated blood pressure.
“The comprehensive safety analysis revealed that contrary to concerns regarding malignancy, venous thromboembolism, and major adverse cardiac events, use of JAK inhibitors was not associated with a significant increase in the overall risk in patients with AD," said Kim. "Therefore, we believe that understanding and managing common adverse events is the need of the hour, particularly those like headache, acne, and nausea, among others."
Kim continued, "Insights gained from this research could lead to refined treatment guidelines and personalized therapeutic strategies, enhance the confidence in prescribed treatments in terms of safety and efficacy and enhance the quality of life for patients with AD."