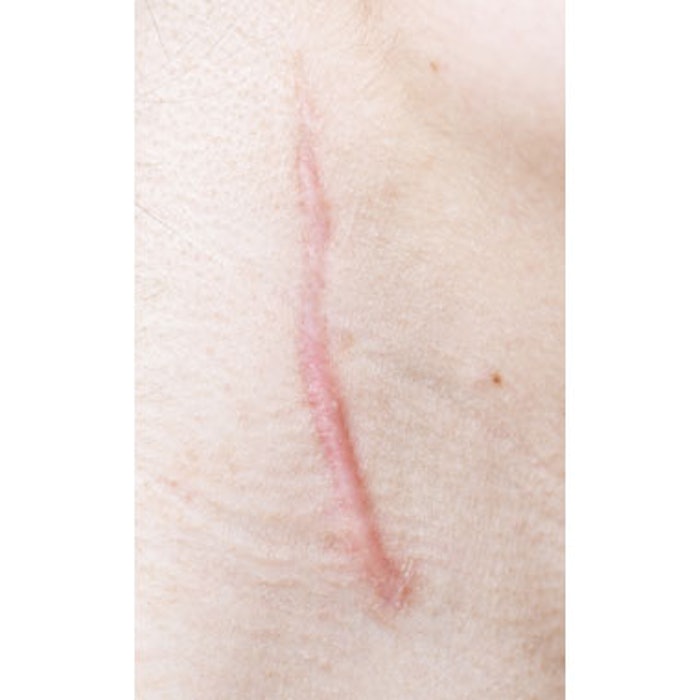
Incision sites treated with RXI-109, a self-delivering RNAi compound from biotechnology company RXi Pharmaceuticals, following scar revision surgery achieved better scores than control incision sites in the same subjects three months after scar revision surgery. Results were rated by a blinded panel and investigator review.
In the first two arms of the ongoing Phase 2a study, 15 subjects received six intradermal injections of RXI-109—eight received 5mg/cm and seven received 10mg/cm—beginning two weeks after scar revision surgery, with the last of the six doses administered three months after surgery. One portion of the revised scar was treated with RXI-109, while the rest of the scar was revised but left untreated. Subjects were assessed using four different evaluation methods: Physician and Observer Scar Assessment Scale (POSAS), Visual Analogue Scale (VAS), a blinded assessment of photographs of the revision sites, and a separate assessment of photographs of the revision sites by a blinded panel separate from the investigators.
Overall, the RXI-109 treated revision sites scored statistically significantly better than the untreated revision sites in all four three-month evaluations. Both dose levels of RXI-109 were equally well tolerated with occasional transient redness and itching occurring in both. The higher dose of 10mg/cm did not appear to add clinical benefit over the 5mg/cm dose, leading to the conclusion that the next cohorts in this ongoing RXI-109-1402 study will be treated with the lower dose. Subsequent cohorts will include evaluation of additional treatments through six months.
“We are very pleased with the outcome of the three-month evaluation of our ongoing Phase 2a study with RXI-109 for the treatment of hypertrophic scars following scar revision surgery,” said Geert Cauwenbergh, MD, president and CEO of RXi Pharmaceuticals. “Not only do these four different evaluation methods confirm the same positive conclusion, the results also bring us another step closer to identifying the final treatment schedule for RXI-109 in the management of surgical incision sites in subjects prone to hypertrophic scarring. Our continued clinical development will now focus on identifying the optimum treatment length using the 5mg/cm dose.”
Photo copyright Getty Images.