Men with melanoma are more likely to die than women with melanoma, especially men with skin of color, according to an article published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology (JAAD).
Related: DermTech Melanoma Test Now Covering 9M Additional Lives with Veteran’s Health Association
The analysis involved more than 200,000 participants and is the largest study to date on racial differences in men with melanoma. It compared melanoma diagnosis data from the National Cancer Database from 2004 until 2018 in White, Black, Asian, American Indian/Alaskan Native and Hispanic men.
Overall survival rates in men with melanoma were highest for White men (75%), followed by American Indian/Alaskan Native (69%), Asian (68%), Hispanic (66%) and Black men (52%). White and American Indian/Alaskan Native men were more likely to develop melanoma on the trunks of their bodies, while Black, Asian and Hispanic men were more likely to develop it in their lower extremities, and Black, Hispanic and Asian men are more likely to have melanoma diagnosed at an advanced stage when it is more difficult to treat, specifically areas that are not exposed to the sun, according to the report.
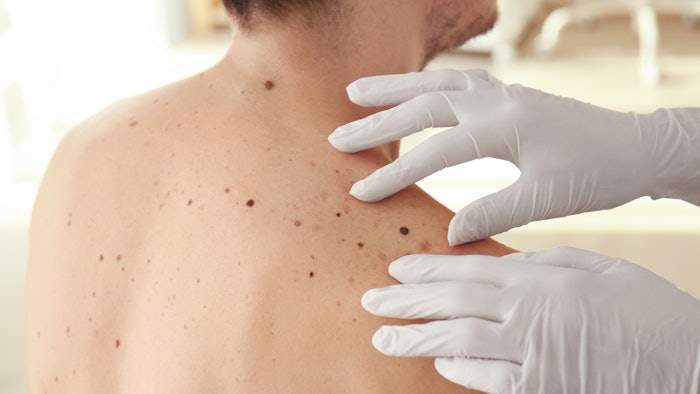
To perform a skin self-exam, check the skin and nails for the following:
- Asymmetry: One half of the spot is unlike the other half.
- Border: The spot has an irregular, scalloped, or poorly defined border.
- Color: The spot has varying colors from one area to the next, such as shades of tan, brown or black, or areas of white, red, or blue.
- Diameter: While melanomas are usually greater than 6 mm, or about the size of a pencil eraser, when diagnosed, they can be smaller.
- Evolving: The spot looks different from the rest or is changing in size, shape, or color.
Ashley Wysong, M.D., F.A.A.D., founding chair of the Department of Dermatology at the University of Nebraska Medical Center and co-author of the study, said, "We know that men may be less likely to seek medical care than women, so they can be diagnosed with melanoma at later stages. However, even after accounting for later stages at diagnosis, men still have worse overall survival rates than women with melanoma, so we suspect that there are some unmeasured social, genetic, tumor-specific and potentially biological factors at play, such as hormones and the way the immune system responds to melanoma tumors."
Dr. Wysong continued, "The location of the first diagnosed melanoma can play a role in this issue. Many patients have spots evaluated by dermatologists because somebody else has pointed out a spot to them. Melanoma in areas that do not have sun exposure can be more difficult for both patients and their loved ones to see, which can lead to a delayed diagnosis. In addition, melanoma in patients with darker skin tones can often be mistaken for other skin conditions, which can also delay care and definitive treatment. We hope our research can lay the foundation for future studies to determine why there's such a gap in survival rates, and to make headway to reduce these survival rate gaps,"