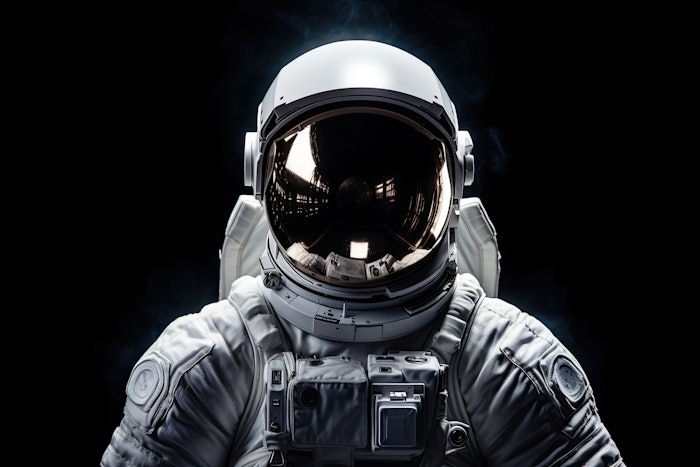
Aesthetics, a field of healthcare reserved for alleviating cosmetic concerns and restoring wellness, is demonstrating practicality for astronauts when they return from space exploration. Born from BTL Aesthetics’ partnership with the Hungarian To Orbit program, Emsculpt Neo—known for body contouring—played a role in preparing Tibor Kapu, a Hungarian research astronaut, for an upcoming mission aboard the International Space Station.
This article is only available to registered users.
Log In to View the Full Article
Aesthetics, a field of healthcare reserved for alleviating cosmetic concerns and restoring wellness, is demonstrating practicality for astronauts when they return from space exploration. Born from BTL Aesthetics’ partnership with the Hungarian To Orbit program, Emsculpt Neo—known for body contouring—played a role in preparing Tibor Kapu, a Hungarian research astronaut, for an upcoming mission aboard the International Space Station.
According to NASA, astronauts experience muscle and bone atrophy because their bodies no longer bear Earth’s gravity—bone breakdown outpaces growth and muscles weaken from lack of use [1]. Emscult Neo is a non-invasive muscle-stimulation technology that uses radiofrequency heating to reduce fat and high-intensity, focused electromagnetic energy, simultaneously, to build muscle. Per an Oct. 20 press release, the Neo device helped support Kapu’s endurance, strength, balance and recovery.
The Emsculpt Neo procedure involves lying down while applicators are attached to the treatment area, and patients may feel a warming sensation along with intense muscle contractions. Electromagnetic treatments were cleared by the US Food and Drug Administration in 2017 for strengthening, firming and toning the abdomen, buttocks, thighs, arms and calves [2].
Electromagnetic muscle stimulation has been used for decades in physical therapy—used to treat incontinence by strengthening the pelvic muscles, and has also been used to reduce postoperative pain and edema after plastic surgery, although the science is limited [2]. The Emsculpt device was manufactured in 2019, two years after FDA clearance.
"Studies show astronauts lose up to 30% of muscle mass in orbit, depending on the duration of the mission. Emsculpt Neo has been an essential part of physical conditioning and rehabilitation, helping us maximize both muscle performance and recovery," said Nóra Sydó, a cardiologist and sports medicine specialist, who led the astronaut training team.
References:
1-https://www.nasa.gov/missions/station/iss-research/counteracting-bone-and-muscle-loss-in-microgravity/
2-https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9869942/