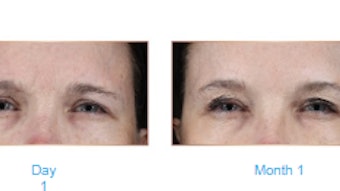
A study conducted in May 2022 revealed microinjections with glycerol and hyaluronic acid can have potential skin health benefits. The study, detailed in Skin Research & Technology by Linda Kleine-Börge, et. al., involved providing single-dose and multiple-dose treatments of CPM-HA20G (Belotero Revive) to 15 women to observe the changes in biomechanical viscoelastic skin properties. The data showed that the CPM-HA20G microinjections can improve skin firmness and fatigue, with stronger and more pronounced results with multiple treatments.
Related: Hyaluronic Acid Fillers: Review of Delayed Complications
For the study, 26 subjects were enrolled on-site, 25 women and one man, but due to gender-related significant differences in the measurement parameters, only data of fertile female subjects of Fitzpatrick skin type II–V were evaluated for this investigation. Of the 15 participants, five women with a mean age of 42 and body mass index of 24 received a single treatment and 10 women with a mean age of 34 and body mass index of 23 were given multiple treatments.
The subjects were injected at the dermal level into the lower cheeks, with treatments provided four weeks apart. Both single-treatment and multiple-treatment methods were observed. Biophysical measurements were performed describing the viscoelastic skin properties and the underlying skin structure before injection and on follow-up visits every four weeks.
Related: Microbotox Treats Acne and Rosacea with High Patient Satisfaction
Both treatment methods showed statistically significant improvements in skin firmness, skin fatigue and skin density. The skin firmness parameter of the single-treatment group increased by 1% from baseline to week 16 and the multiple-treatment group decreased by 15%. There were zero-to-weak correlations between skin thickness and biomechanical skin properties
Results from the study suggest that a single injection treatment can have clinical value for skin with good skin quality and only a slight need for optimization, with another treatment after 24-36 weeks. Skin needing a more pronounced quality improvement should consider multiple microinjection treatments, with a touch-up treatment after 64 weeks.