Tretinoin delivered via a nano lipid carrier drug delivery system provided faster clearance of acne lesions and reduced the intensity of porphyrin production in the pilosebaceous follicles compared to a conventional tretinoin topical.
Related: Micro-plasma RF vs. RF Microneedling for Acne
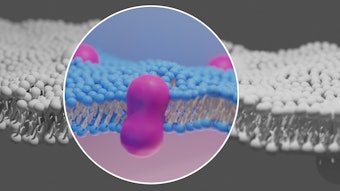
For a split-face study published in the Archives of Dermatologic Research (June 19, 2021), Aniseh Samadi, et al, assessed the efficacy and safety of a nano lipid carrier (NLC) drug delivery system containing tretinoin (NLC-TRE) in comparison with the conventional 0.05% tretinoin cream (TRE cream) in mild to moderate acne vulgaris.
They used a high-pressure homogenizer to create a stable NLC-TRE formulation and performed a randomized split-face study. The spherical nanoparticles had a particle size of 118.5 nm, PI equal to 0.485 and ZP of − 44.7 mV.
Related: Extractions vs. Oral Doxycycline for Acne
The investigators assessed the number of acne lesions, porphyrin production and skin biophysical parameters in both sides of the face following treatment. In addition, they measured the plasma concentration of tretinoin after topical application of NLC-TRE for primary safety evaluation.
The rate of decrease of acne lesions was significantly higher in NLC-TRE side. The size and intensity of porphyrin production in pilosebaceous follicles were significantly reduced only on the NLC-TRE side. The plasma concentration of the tretinoin, after eight weeks of application remained lower than the toxic levels.